According to Unesco, adult illiteracy is defined as the percentage of the population aged 15 years and over who cannot both read and write with understanding a short simple statement on his/her everyday life.
A high literacy rate (or low illiteracy rate) suggests the existence of an effective primary education system and/or literacy programmes that have enabled a large proportion of the population to acquire the ability of using the written word (and making simple arithmetic calculations) in daily life and to continue learning. It is common practice to present and analyse literacy rates together with the absolute number of adult illiterates as improvements in literacy rates may sometimes be accompanied by increases in the illiterate population due to the changing demographic structure.
In the latest Demographic and Health Survey, while adult literacy has in Nigeria adult literacy rate has increased from 51.1% in 2008 to of 62 % in 2018, there still seems to be disparity between the regions in the number part of the country as opposed to the south as shown in the graphs below.
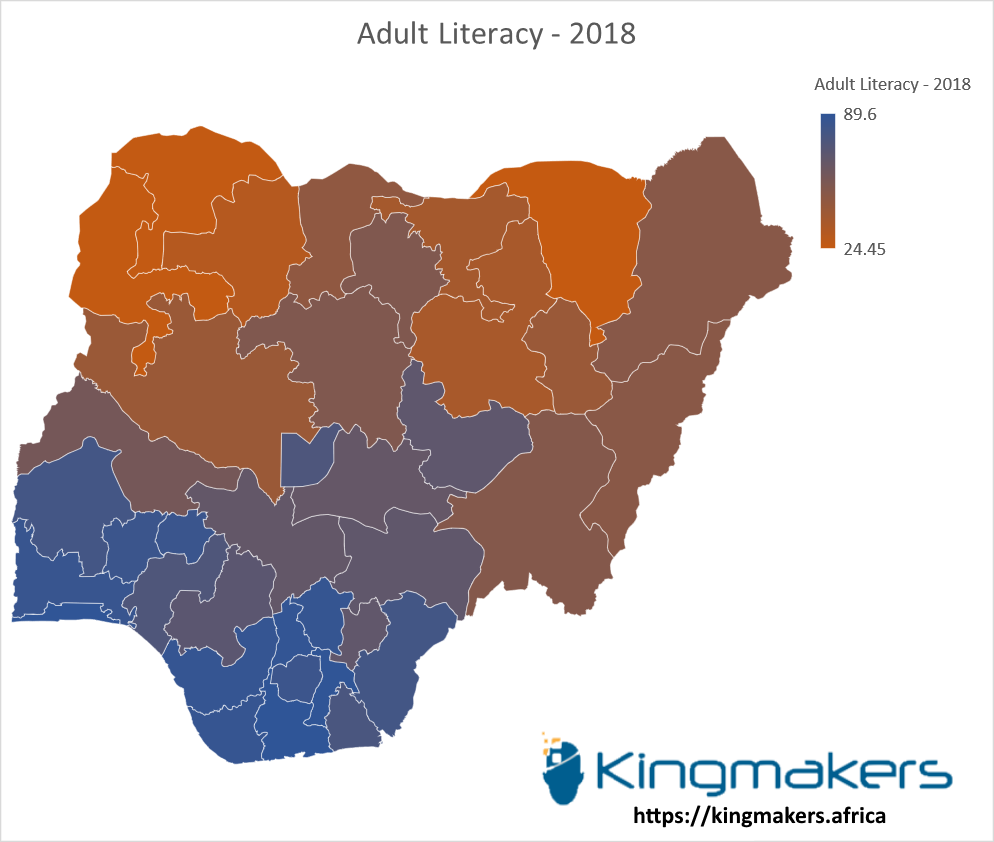
Adult Literacy by States in Nigeria - 2018
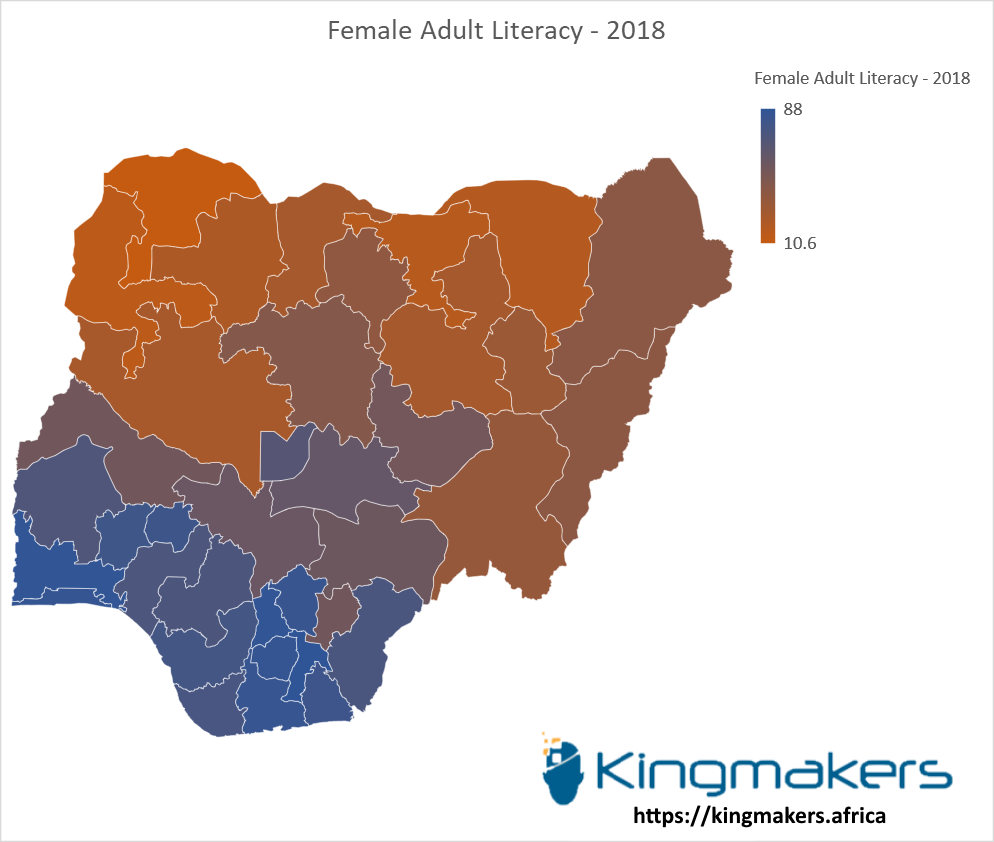
Female Adult Literacy by States in Nigeria - 2018
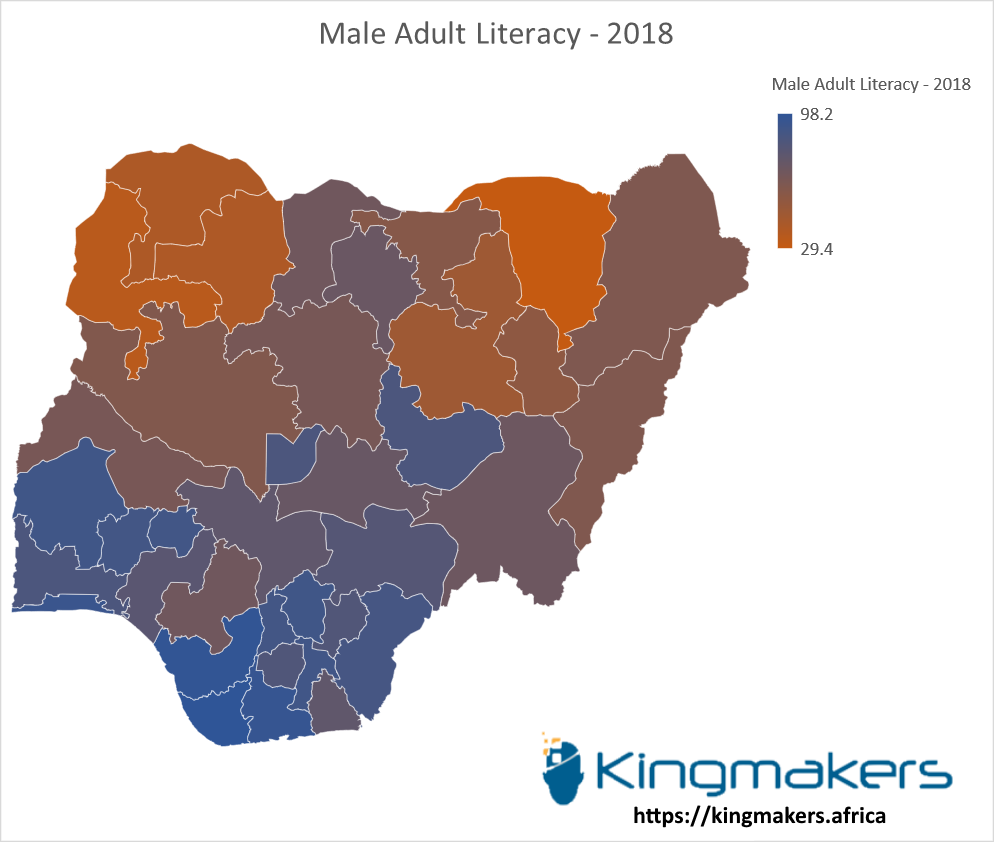
Male Adult Literacy by States in Nigeria - 2018